8. Debugging (Visual Studio Code)
Here is an example of stepping through Python code executed by MPI using Visual Studio Code (hereinafter referred to as VS Code). Step execution can be performed by attaching a debugger to a rank 0 process among the processes running in MPI parallel.
Warning
In the debugging using debugpy described here, communication is performed between VS Code and the compute node executing the code to be debugged, but the communication port on the compute node side is an any connection, which is accessible even to the person who is not debugging. Please understand that before using it. Also, please do not access the compute node other than the one you have reserved.
8.1. Installing
In your local environment, follow the VS Code web page (https://code.visualstudio.com) to install VS Code. After installing VS Code, install a extension function “Remote - SSH”.
8.2. Running Interactive Job
Log in to the login server and run the Interactive job. This example uses two compute nodes.
(Since the number of compute nodes is limited, please exit the Interactive job with the exit command when you are finished.)
[user1@loginvm-XXX ~]$ salloc -N 2 -p Interactive --time=1:00:00
[user1@fx-XX-XX-XX ~]$
8.3. Connecting to the Login Server from VS Code
Connect to the compute node from VS Code using Remote - SSH. Press the F1 key and search for and select Remote-SSH: Connect to Host.
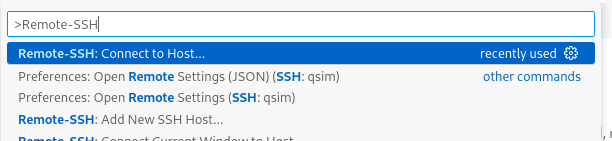
Enter qsim in the next dialog.
This completes the connection from VS Code to the login server.
Note
The initial connection takes a long time to complete because the VS Code server is installed on the remote host.
8.4. Stepping with VS Code
~/example created in Job Execution Method as an example.~/example .
8.4.1. Preparation
8.4.1.1. Installing Python extensions
Install the following Python extension in VS Code.

8.4.1.2. Creating a VS Code configuration file
Create ~/example/.vscode/launch.json with the following content.
Note that host should be the host name (fx-XX-XX-XX) of the compute node assigned in the Interactive job.
Note
From now on, each time you run an Interactive job, you must edit the host in the configuration file to match.
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Python: remote connection",
"type": "python",
"request": "attach",
"connect": {
"host": "fx-XX-XX-XX",
"port": 5678
},
"pathMappings": [
{
"localRoot": "${workspaceFolder}",
"remoteRoot": "${workspaceFolder}"
}
],
"justMyCode": true
}
]
}
8.4.1.3. Creating a job file
Create ~/example/job_debug.sh with the following content.
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# Usage:
# srun -n 2 job_debug.sh <path/to/venv> <python file>
#
# Example:
# srun -n 2 job_debug.sh ~/example/qenv example.py
# Environment variable settings required for using MPI in a quantum simulator system
export UCX_IB_MLX5_DEVX=no
export OMP_PROC_BIND=TRUE
# Number of threads used for OpenMP parallelization
# Due to the OpenMP multi-threading behavior, some libraries (such as scipy) can introduce small calculation errors,
# which can lead to inconsistent calculation results between processes during MPI execution. When using mpiQulacs, set it to 1.
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=1
# Number of threads used by mpiQulacs (if not set, the value of OMP_NUM_THREADS is used)
export QULACS_NUM_THREADS=48
# Activating Python virtual environment
source $1/bin/activate
shift
### Workaround for the glibc bug (https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1722181)).
if [ -z "${LD_PRELOAD}" ]; then
export LD_PRELOAD=/lib64/libgomp.so.1
else
export LD_PRELOAD=/lib64/libgomp.so.1:$LD_PRELOAD
fi
# Executing a Python command
RANK=${PMIX_RANK}
if [ ${RANK} -eq "0" ]; then
COM='python -m debugpy --listen 0.0.0.0:5678 --wait-for-client'
else
COM='python'
fi
${COM} "$@"
Open a terminal in VS Code and grant execute permission to ~/example/job_debug.sh .
chmod u+x ~/example/job_debug.sh
8.4.1.4. Installing debugpy
Install debugpy in a virtual environment for Interactive jobs.
[user1@fx-XX-XX-XX ~]$ cd example
[user1@fx-XX-XX-XX example]$ source ./qenv/bin/activate
(qenv) [user1@fx-XX-XX-XX example]$ pip install debugpy
8.4.2. Step execution
~/example/example.py in VS Code.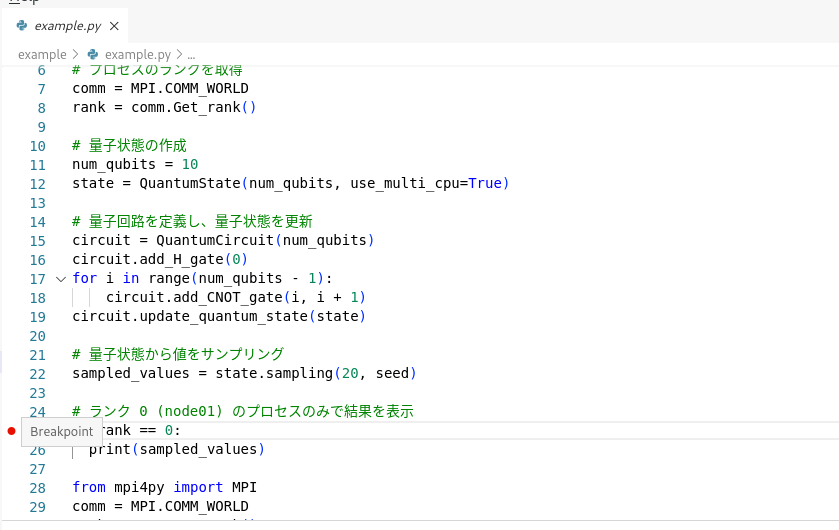
Then, in the Interactive job virtual environment, do the following.
(qenv) [user1@fx-XX-XX-XX example]$ srun -n 2 job_debug.sh ~/example/qenv example.py
Note
Note that the arguments are different from job.sh created in Job Execution Method .
The job_debug.sh takes a path to a Python virtual environment (~/example/qenv) and a Python file to debug.
(The command python is listed in job_debug.sh, so you do not need to specify it as an argument.)

After a pause, the execution of the rank 0 process pauses when it reaches the breakpoint.
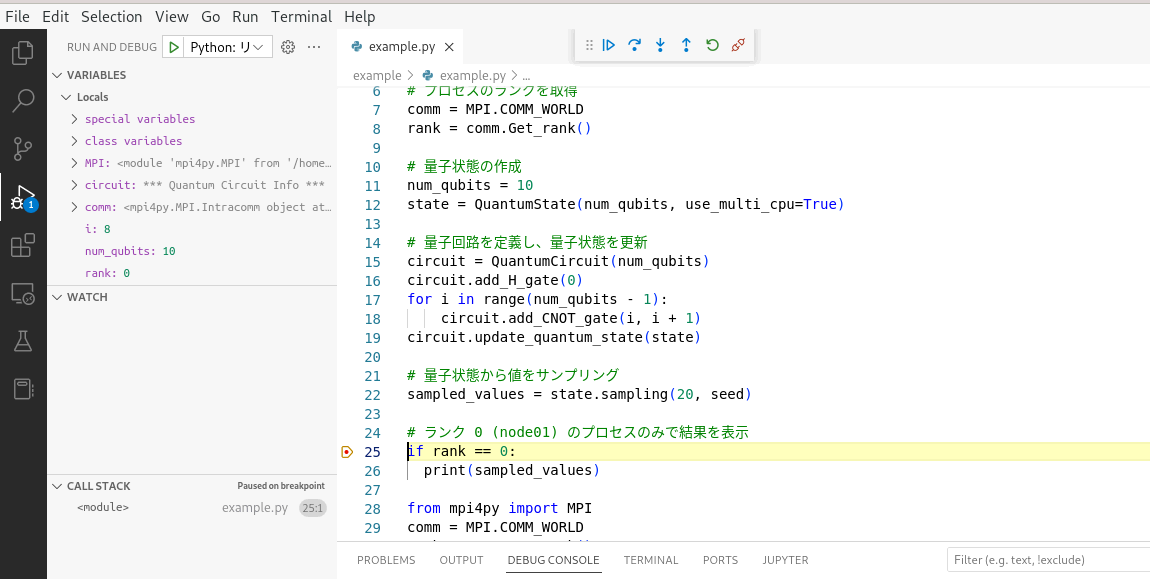
In this state, steps can be performed from the toolbar shown below on VS Code.