1. System Overview
1.1. System Configutation
The Quantum Simulator System consists of compute nodes for simulation (consisting of 512 FX 700), a jump server for login, a login server for job submission, a shared directory, a job scheduler, a private PyPI repository, a document server, and a proxy server for Internet access.

The user logs in to the login server through the jump server. The compute nodes are available from the login server through the job scheduler Slurm. The compute nodes are connected by InfiniBand, and the quantum circuit is simulated while performing parallel calculation using MPI (Message Passing Interface).
The role and IP address/hostname of each server
Name |
IP / Host |
Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Jump Server |
106.184.62.10
Port number: Notification from Fujitsu
|
Server in a DMZ |
Login Server |
login-server |
User environment for utilizing computation
Accessible from the jump server
|
Compute Node |
N/A |
Cluster system for executing quantum program
|
Shared Directory |
N/A |
Directory for placing files shared between compute nodes |
Private PyPI Repository |
simulator-pypi |
Private Python package repository for Fujitsu software packages (e.g. mpiQulacs) |
Document Server |
simulator-docs |
Server that contains updated information and API manuals |
HTTP Proxy Server |
simulator-proxy |
Proxy server used to access Internet from the compute node |
Specifications for each server/node
Server name |
Item |
|
|---|---|---|
Login Server |
OS |
Rocky Linux 8.6 |
CPU |
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6348 (2.6GHz) x 1core |
|
Memory |
32GB |
|
Compute Node |
OS |
Rocky Linux 8.5 |
CPU |
Fujitsu A64FX (2.0GHz) x 48cores |
|
Memory |
32GB |
|
Shared Directory |
File System |
GlusterFS |
Storage Capacity |
3TB/group |
Note
Use the jump server only as a relay to access the login server. Do not create or execute programs on the jump server.
Note
The initial storage capacity of the shared directory is 3 TB, but if you still run out of space after deleting unnecessary files, contact your Fujitsu representative.
1.2. Job Scheduler
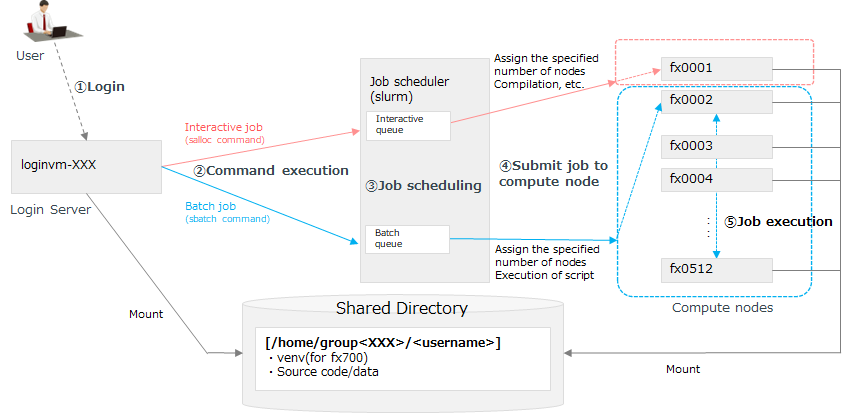
Note
The home directory of each user’s login server mounts the shared directory. The same directory is mounted on all compute nodes.
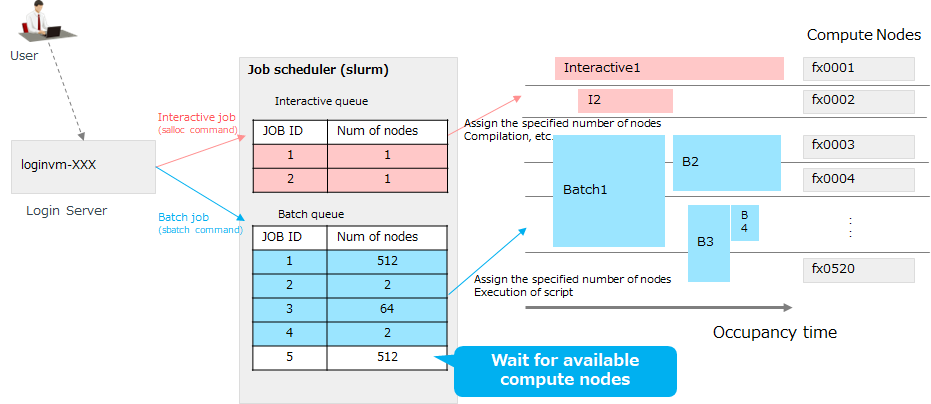
Note
The number of nodes used and the maximum number of qubits are as follows, and quantum circuits up to 39 qubits can be executed when 512 nodes are used.
Number of nodes used |
512 |
256 |
128 |
64 |
32 |
16 |
8 |
4 |
2 |
1 |
Maximum qubit number |
39 |
38 |
37 |
36 |
35 |
34 |
33 |
32 |
31 |
30 |