Usage
from qiskit_qulacs import QulacsProvider
backend = QulacsProvider().get_backend()
# type(backend) --> qiskit_qulacs.QulacsBackend
Examples
Example 1 : implementation of quantum circuits by execute(…)
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit, execute
from qiskit_qulacs import QulacsProvider
from mpi4py import MPI # If you do not use MPI classes, you do not need to write this (this is done internally by qiskit_qulacs import).
# Get rank in MPI
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
rank = comm.Get_rank()
# Create quantum circuits
num_qubits = 10
circ = QuantumCircuit(num_qubits)
circ.h(0)
for i in range(num_qubits - 1):
circ.cx(i, i + 1)
circ.measure_all()
# Run quantum circuits
if rank == 0:
print('Execute a circuit of 10 qubits.')
backend = QulacsProvider().get_backend() # Get QulacsBackend instance
job = execute(circ, backend=backend, shots=1024, memory=True, seed_transpiler=50, seed_simulator=80)
result = job.result()
# Display results
if rank == 0:
counts = result.get_counts()
print(f'{counts=}')
# memory = result.get_memory()
# print(f'{memory=}')
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -p Batch # Specify Batch queue
#SBATCH -o test # Output file name
#SBATCH -N 2 # Number of nodes allocated
#SBATCH -t 06:00:00 # max execution time
mpirun -npernode 1 job.sh ~/example/qenv python example1.py
$ sbatch sim_example1.job
$ cat ./test
counts={'0000000000': 511, '1111111111': 513}
# memory=['0000000000', '1111111111', ...] # Results per shot (available in execute(...) with memory = True)
Example 2 : use of QuantumInstance
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit
from qiskit.algorithms import VQE
from qiskit.algorithms.optimizers import SPSA
from qiskit.circuit.library import TwoLocal
from qiskit.opflow import I, X, Z
from qiskit.utils import QuantumInstance, algorithm_globals
from qiskit_qulacs import QulacsProvider
from mpi4py import MPI # If you do not use MPI classes, you do not need to write this (this is done internally by qiskit_qulacs import).
# Get rank in MPI
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
rank = comm.Get_rank()
algorithm_globals.random_seed = 50
# Hamiltonian for an H2 molecule
H2_op = (-1.052373245772859 * I ^ I) + \
(0.39793742484318045 * I ^ Z) + \
(-0.39793742484318045 * Z ^ I) + \
(-0.01128010425623538 * Z ^ Z) + \
(0.18093119978423156 * X ^ X)
backend = QulacsProvider().get_backend() # Get QulacsBackend instance
qi = QuantumInstance(backend=backend, seed_transpiler=1234, seed_simulator=20)
ansatz = TwoLocal(rotation_blocks='ry', entanglement_blocks='cz')
spsa = SPSA(maxiter=125)
vqe = VQE(ansatz, optimizer=spsa, quantum_instance=qi)
# Run VQE
if rank == 0:
print('Run VQE with Qiskit and mpiQulacs')
result = vqe.compute_minimum_eigenvalue(operator=H2_op)
# Display results
if rank == 0:
print(f'VQE result is {result.eigenvalue.real:.5f}')
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -p Batch # Specify Batch queue
#SBATCH -o test # Output file name
#SBATCH -N 2 # Number of nodes allocated
#SBATCH -t 06:00:00 # max execution time
$ mpirun -npernode 1 job.sh ~/example/qenv python example2.py
$ sbatch sim_example2.job
$ cat ./test
VQE result is -1.85719
Specify Random Seed
from qiskit.utils import QuantumInstance, algorithm_globals
algorithm_globals.random_seed = integer value
execute(circuit, seed_transpiler=integer value, seed_simulator=integer value)
# If QuantumInstance is used instead of execute(...):
# qi = QuantumInstance(backend=backend, seed_transpiler=integer value, seed_simulator=integer value)
As in the above example, always specify a seed value if you can set a random seed. (example: qiskit.quantum_info.random_unitary(dims, seed))
Note
quantum_instance parameters, such as qiskit.algorithms.VQE(…), accept a Backend object as well as a QuantumInstance object, but remember to specify a QuantumInstance object because a Backend object prevents you from specifying values of seed_transpiler and seed_simulator.
Basis Gates
QulacsBackend supports the following as basis gates:.
Unitary operations
x, y, z, h, s, sdg, t, tdg, rx, ry, rz, u1, u2, u3, u, p, id, sx, sxdg, cx, cz, swap
Non-unitary operations
measure, reset, barrier
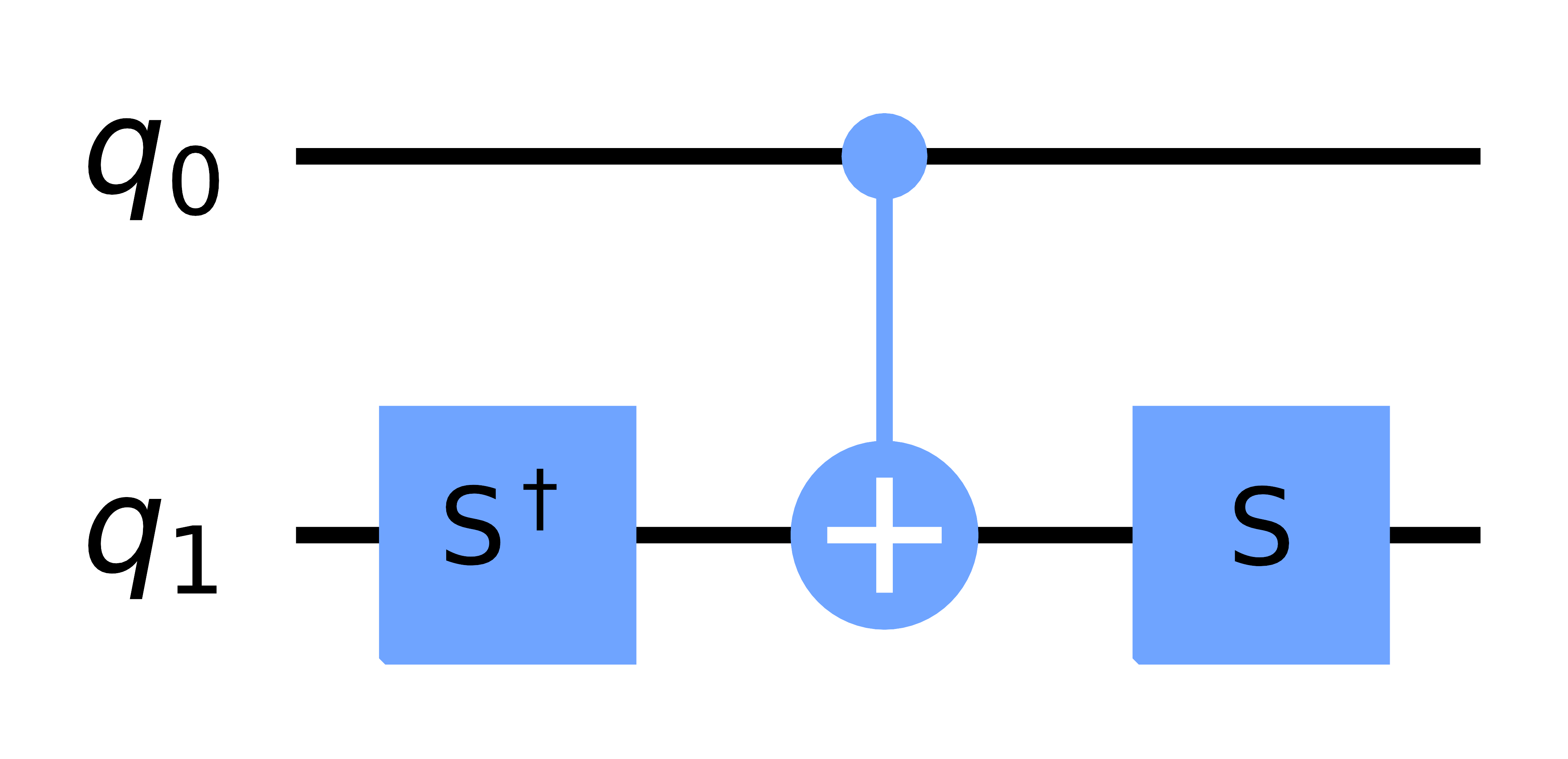
(reference) You can see how circuits are transpiled as follows.
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit, transpile
from qiskit_qulacs import QulacsProvider
circ = QuantumCircuit(2)
circ.cy(0, 1)
backend = QulacsProvider().get_backend()
transpiled_circ = transpile(circ, backend=backend)
print(transpiled_circ.draw(fold=-1))
transpile result
Conditional Gates
QulacsBackend supports conditional gate operations based on classical register values (Qiskit c_if(…) method).
from qiskit import ClassicalRegister, QuantumCircuit, QuantumRegister, execute
from qiskit_qulacs import QulacsProvider
qreg = QuantumRegister(2)
creg = ClassicalRegister(2)
circ = QuantumCircuit(qreg, creg)
circ.h(0)
circ.measure(qreg, creg)
circ.x(1).c_if(creg, 0)
circ.measure(qreg, creg)
backend = QulacsProvider().get_backend()
counts = execute(circ, backend, shots=1024, seed_transpiler=50, seed_simulator=80).result().get_counts()
print(counts)
{'10': 503, '01': 521}
Optimization
When using QulacsBackend, there are two types of circuit optimization:.
Optimization by Qiskit transpile(…) method
When the quantum circuit is executed via execute(…) and QuantumInstance, the transpile(…) method is called internally for optimization. The optimization level can be controlled by the value of the optimization_level parameter for execute(…) and QuantumInstance(…). See documents of Qiskit transpile(…) for details.
Optimization by Qulacs QuantumCircuitOptimizer
After optimization with transpile(…) above, further optimization is done with Qulacs’s QuantumCircuitOptimizer. (Reference: documents of Qulacs QuantumCircuitOptimizer) You can control the optimization level with a set_qulacs_optimization (mode, block_size, swap_level) method of the QulacsBackend instance. You can also get the current settings with the get_qulacs_optimization() method. A description of each parameter follows:.
Parameter |
Explanation |
|---|---|
mode |
Ether None, ‘normal’, ‘light’ can be set. (Default is ‘light’.)
If None is specified, no optimization is performed by QuantumCircuitOptimizer.
Specify ‘normal’ or ‘light’ to perform optimizations by QuantumCircuitOptimizer optimize or optimize_light method, respectively.
|
block_size |
If mode is’ normal ‘, QuantumCircuitOptimizer().optimize(circuit, block_size, swap_level) is executed using the value specified for block_size.
See API specifications of mpiQulacs for possible block_size values.
If mode is None or ‘light’, the value of the block_size argument is ignored.
|
swap_level |
If mode is’ normal ‘or’ light ‘, the optimize(circuit, block_size, swap_level) or optimize_light(circuit, swap_level) of QuantumCircuitOptimizer is executed using the value specified in swap_level.
See API specification of mpiQulacs for the meaning of swap_level.
The default is swap_level = 0 .
If mode is None, the value of the swap_level argument is ignored.
|
Note
If a quantum circuit includes operations that involve measurements in the middle (excluding the measurement operation performed at the end of the circuit), the QuantumCircuitOptimizer does not optimize, regardless of the value set in mode. (QuantumCircuitOptimizer does not support optimization for such circuits.)
Warning